Bash the most common shell. Zsh is the most popular one among developers. But Fish is the most underrated one.
I am not exaggerating. Fish indeed is an overlooked shell that could be a great fit for beginners and advanced FOSSers alike.
Fish provides a range of features that makes it an attractive choice. From syntax highlight to abbreviation (my favorite), there are numerous novelties here.
Let me share some of my favorite Fish shell features with you.
1. Syntax highlighting
It is better to spot errors before they get executed. This saves a lot of time, energy and frustration.
Most modern code editors have the syntax highlighting built-in. Fish has this functionality built into the shell itself and it works on Linux commands.
Incorrect commands? You see it highlighted in red. The same goes for arguments and options that do not match with the context.

2. Autosuggestions
The Fish shell suggests commands as you type, which you can later complete accordingly using the tab key.

The suggestions will be greyed out as you type, to make it more accessible. If the whole line of suggestion is acceptable to you, you can press the right arrow key to complete it in full.
3. Interactive man page for command options
This is a cool feature, where you will be able to complete a command’s options, by taking help from the man page interactively.
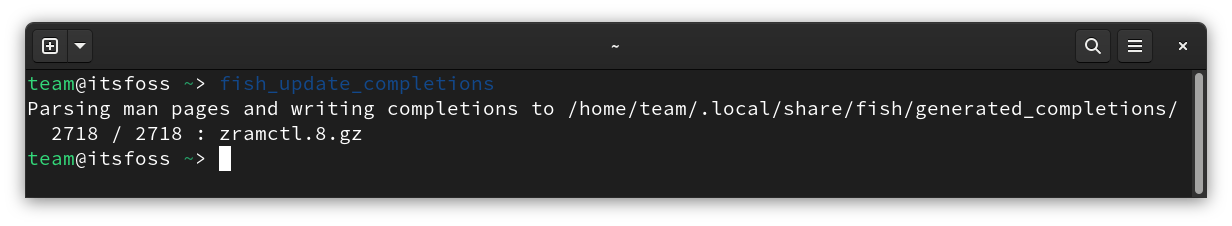
First, you need to parse the man page, which can be done by running:
fish_update_completions
This will parse the man pages.
Now, if you type a command, put a hyphen for the options and then press the tab button to see the man page suggestions for the possible options with their short descriptions:

You can scroll through the options, and select after reading about its work, from the pager that appears.
This makes things a bit more easier than typing command -h.
4. Abbreviations instead of aliases
Abbreviations in Fish are like text-expanders. Here, you will set some frequently used code to an easily accessible abbreviation.
For example, I have used sch as an abbreviation for the command pacman -Ss to search for packages.
abbr -a sch pacman -Ss
Now, whenever I type sch and press the space button, it will be replaced with pacman -Ss.

You can make it permanent by writing it to the config file.
💡
The difference between alias and abbreviation is that an alias works under the hood. You don’t get to see the actual commands it is aliased to. Abbreviation will show the actual commands and they are also recorded into the history correctly.
5. Extensive web-based help
Linux purists rely on the man pages to get help with a command. The newer bunch of Linux users are more reliant on the web for such things.
Fish gives a mix of both with its extensive “web-based” help which is easily available on your system, even if there is no internet, since it is stored locally.
To get help, while running Fish shell, just use:
help
This will open the Help page on your web browser.
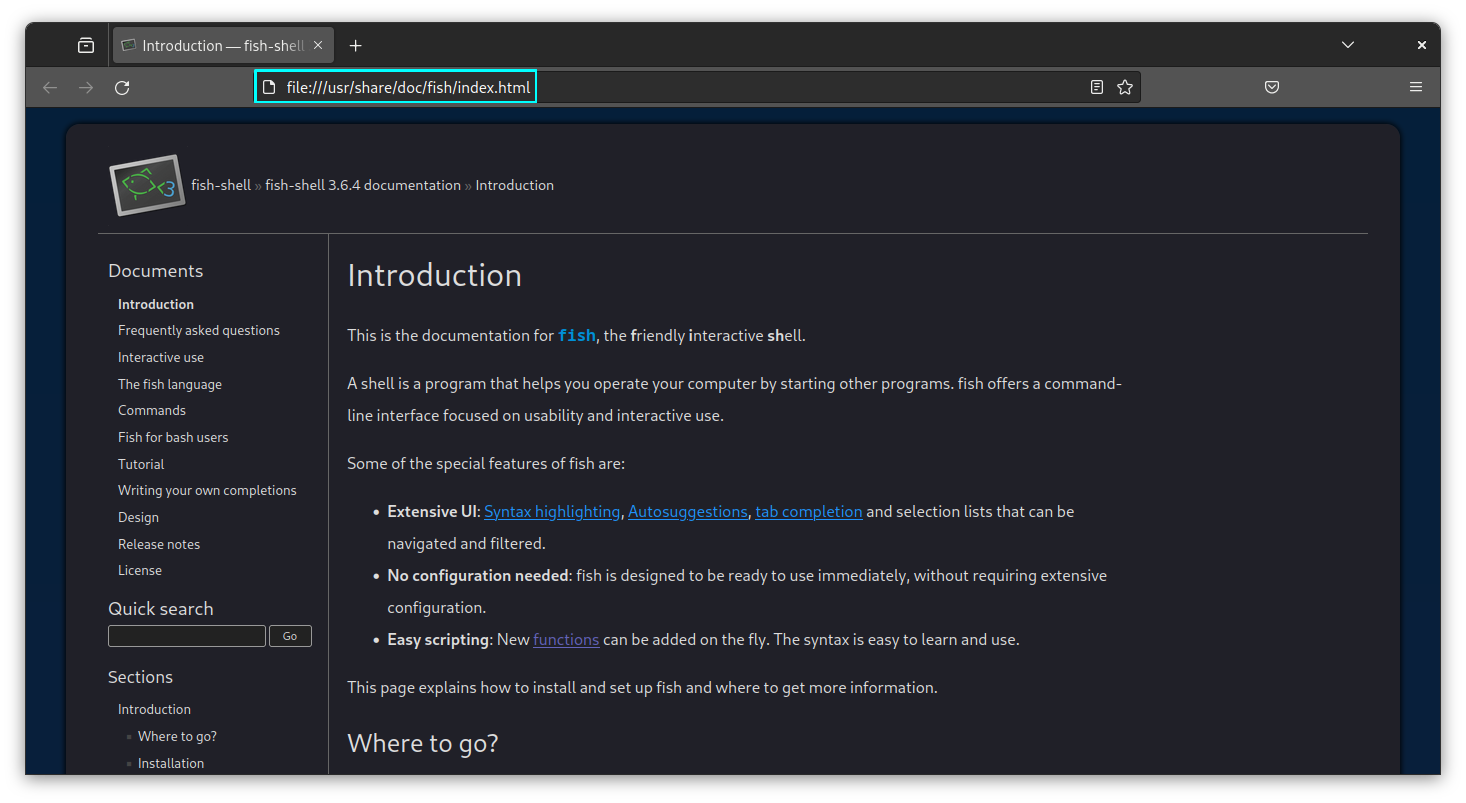
You can refer to the extensive documentation with ease now.
6. Web-based configuration
Yes, another ‘web-based’ feature.
To change the prompt color or other configurations, you don’t need to edit configuration files in the terminal. Instead, you can use the web-based configuration.
Type the following command while running Fish shell:
fish_config
This will open the configuration settings on your browser.
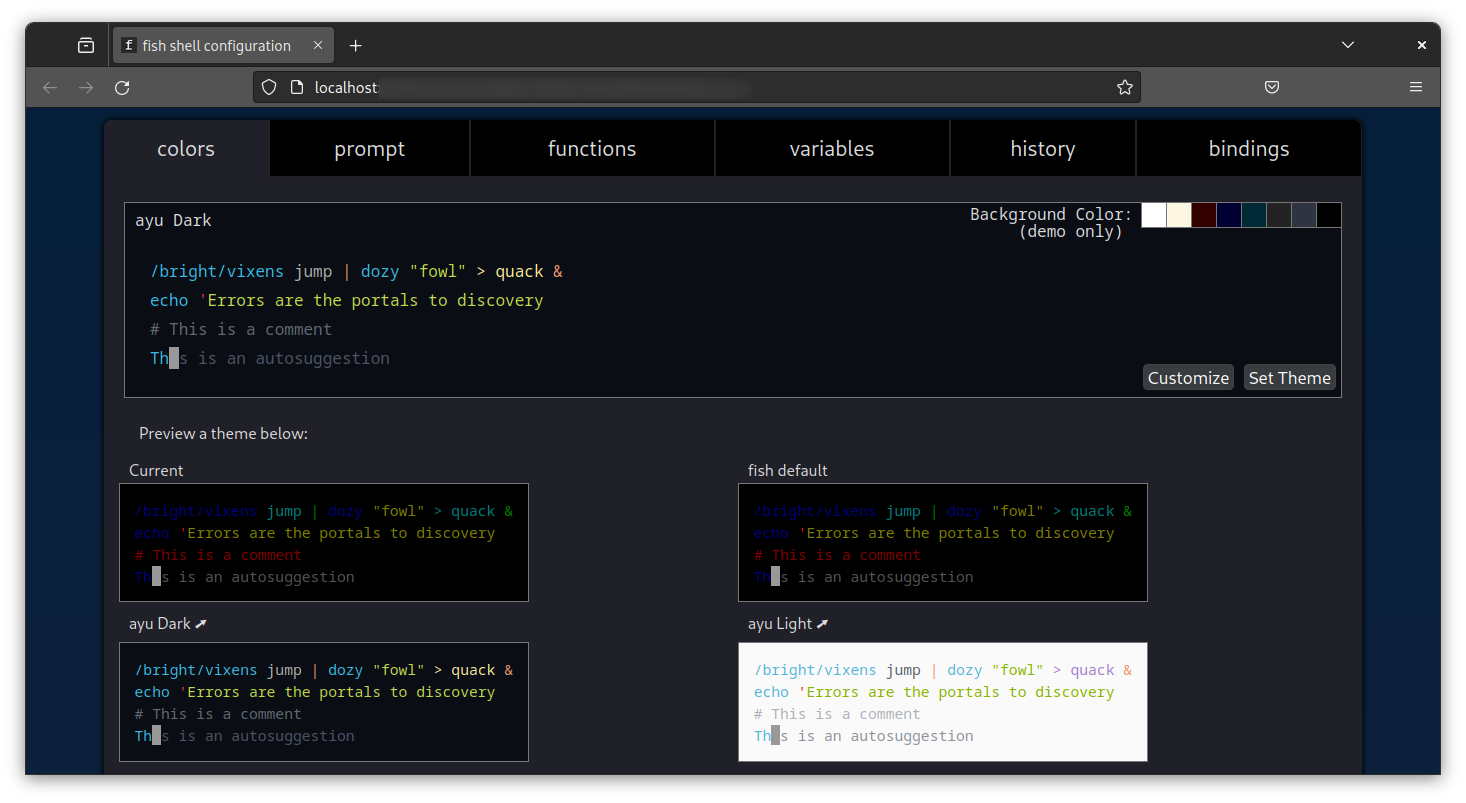
Here, you can change the colors, set a different prompt from the already available list, etc.
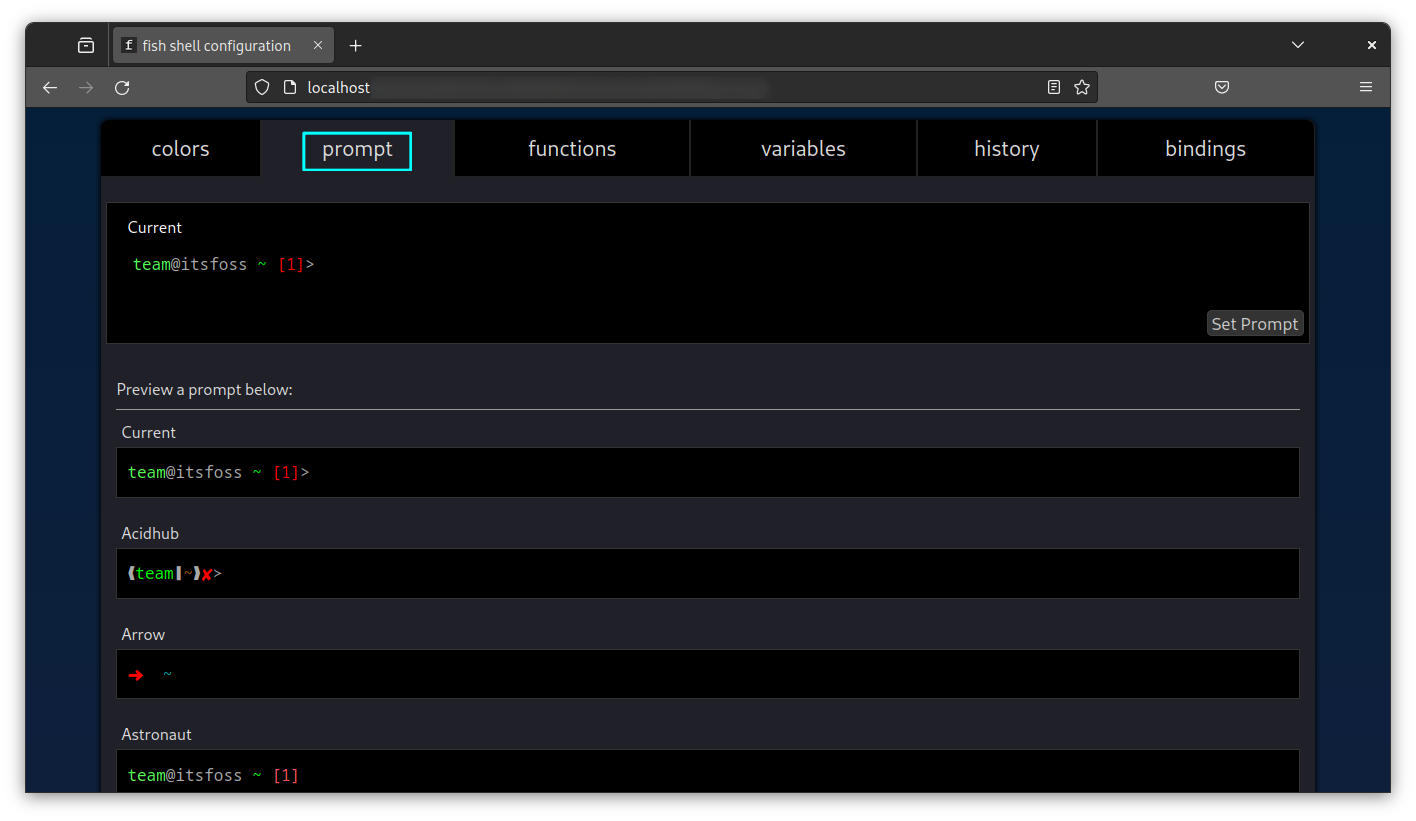
Easier to make changes this way, no?
7. Automatic CD
If you want to move to a directory, you don’t need to type the cd command. Just type the directory name, that’s it.
For example, if you are in your Home directory and want to move to the Downloads directory, just enter Downloads. As you type, it will suggest further completion as well.

cdYou need to use the absolute path, if you are in a particular directory and want to go to an entirely different branch.
8. Easier path navigation
If you need to go back and forth between the directories you have visited, no need to type in the path or use cd .. etc. Just press ALT + Right/Left arrow, to move forward and backward, respectively.

Alternatively, you can type cdh and enter, so that a pager interface will come, where you can use the number corresponding to the directory you want to go back to.

9. Interactive history search
You can search for a specific command in history interactively on Fish. For this, use the good old CTRL+R.
This will open a pager like view, with a search prompt. Enter the command name that you need, and see the result:

10. Universal variables
In Fish shell, if you set a variable as Universal, this will be available even if the shell is restarted or even if the system is rebooted.
To make a universal variable, use:
set -U my_variable 10
The value of my_variable will be saved to 10, even if the system is rebooted.
Yeah, no need to add them to your RC or profile.
11. Private Mode
Fish shell has a private mode where the commands you enter will not be saved to the history or stored on the disk.
To move to a private mode, use the command:
fish -P

Once you have finished your work, you can exit out of private mode by typing exit.

There is a lot more to explore with Fish
Fish shell provides many other user-friendly features like:
- Simple Multiline command edit using ALT+Enter
- Switch between Emacs (default)/Vim keybindings
- A simple and clean syntax for scripting
Of course, you can achieve most of the Fish shell features discussed here with some efforts in other shells as well, but having them enabled by default is a different thing.
Fish could help you be a bit more productive and effective with your development work, given that you are controlling your development environment. Don’t write scripts exclusively for Fish shell that others have to run in Bash. Shell compatibility issues may arise in a shared environment on a multi-user system.
If you liked the features, give Fish shell a try and see how it goes. Maybe you’ll change Fish as your default shell.
Even if you don’t want ‘Fish’ in your terminal, you may like (ASCII) aquarium 😉

💬 Please share your views on Fish shell in the comments 😄