The world of software packages on Linux and other Unix-based systems is quite a savannah: each system has its own singular package management approach, making a hell the life of who has to deal with multiple platforms.
There are Pacman for Arch Linux and derivatives, Alpine Package Keeper (a.k.a. APK), Advanced Package Tool (a.k.a. APT) for Debian GNU/Linux and derivatives, Aptitude, a front-end for APT, Snapcraft for Ubuntu and derivatives, Yellowdog Updater Modified (a.k.a. Yum) for RPM-based systems, Slackpkg for Slackware, Emerge for Gentoo, the guix command on Guix, and nix-env on NixOS, among others, not to mention pkg on FreeBSD, Homebrew for macOS, and Scoop for Windows. Every one of those has its own way of management, forcing you to learn different ways to do the same thing.
In short, it’s really a mess… or is it?
Enter UPT
A developer called sigoden has created a universal tool called Universal Package-management Tool, or UPT for short, able to put things together in this jungle. Once you have it installed, you won’t need to learn another package management’s lifestyle again.
UPT is written in Rust so you need to install Rust and Cargo on Ubuntu or whatever Linux distribution you are using.
I recommend installing the rustup package for your system – GNU/Linux systems usually have a rustup package available in their repositories.
📋
All the following commands are intended to be performed by the root user, unless stated otherwise, so don’t forget to run your sudo -i command.
# On Debian GNU/Linux and derivatives:
apt install gcc make rustup
# On Arch Linux and derivatives:
packman -S gcc make rustup
# On Alpine:
apk add gcc make rustup
rustup-init
source ~/.cargo/env
# On RPM-based systems:
yum install gcc make rustup
# On macOS with Homebrew (not Linux, obviously)
brew install clang make rustup
📋
I use clang instead of gcc, and it works as well for me, you’re just going to need to set your CC and CPP environment variables, if you also want to use it too, to clang and clang++ -E respectively.
After installing rustup, don’t forget to add $HOME/.cargo/bin to your PATH. If you’re using Bash as shell (usually the default shell), you have to add the following line to ~/.bash_profile:
export PATH $HOME/.cargo/bin:$PATH
If your shell is Zsh, you can add the same line above to ~/.zshrc instead. Don’t forget to reload the shell.
Now you can install the upt command tool:
rustup default stable
cargo install upt
If you want to use an administration user (e.g. in the wheel or sudo group), you should perform the same commands above as the administrator user.
All set! Now you have a single package management tool you can use the same way across your systems.
Using UPT
Updating the package manager:
sudo upt update

upt updateInstalling a package:
sudo upt install package_name

Upgrading a package:
sudo upt upgrade package_name

Upgrading all installed packages:
sudo upt upgrade

Removing a package:
sudo upt remove package_name

Searching for a package (vtk for instance):
sudo upt search vtk

If the same package is available in apt (deb), Snap, Flatpak etc., which one should UPT choose while installing? It is determined by the order listed in this table.
To prefer a snap package over another, you can set the UPT_TOOL environment variable. On the bottom of your bashrc file, add the line:
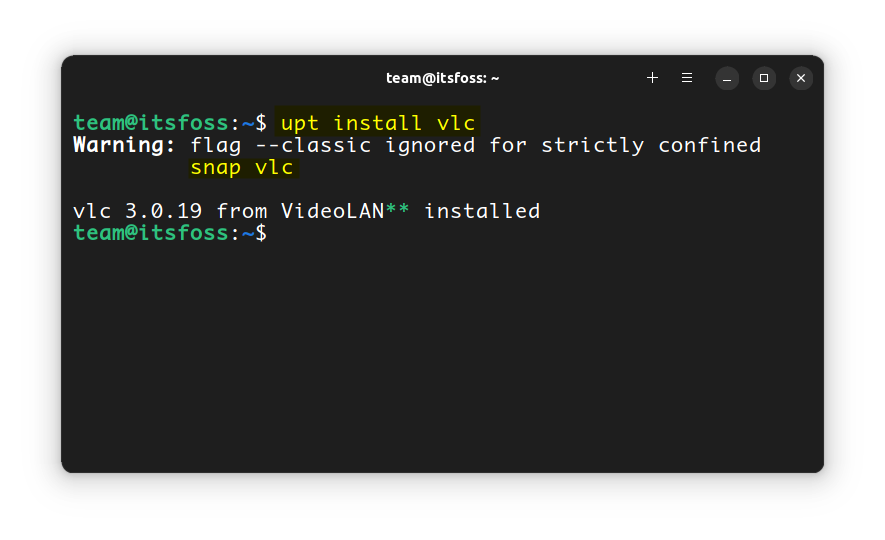
export UPT_TOOL='snap'Now, if you run (do not use sudo on the below command):
sudo upt install vlcIt will prompt for a password. Give it and the snap package will be installed.
Install snap package using UPT
You can see that, the snap version of VLC has been installed.
Conclusion
As you can see, UPT needs initial effort to install, which is not a lot for seasoned Linux users.
Unfortunately, although the package manager is the same across different systems, it’s still a front-end for each system’s default package manager. That means package names are still the same used by each distro, you can’t use a single package name for different systems.
For instance, if you want to install the Python development package, you’ll need different packages for different systems:
# On Alpine, Debian GNU/Linux, and derivatives
upt install python3-dev
# On RPM-based systems:
upt install python3-devel
# On Arch Linux
upt install python
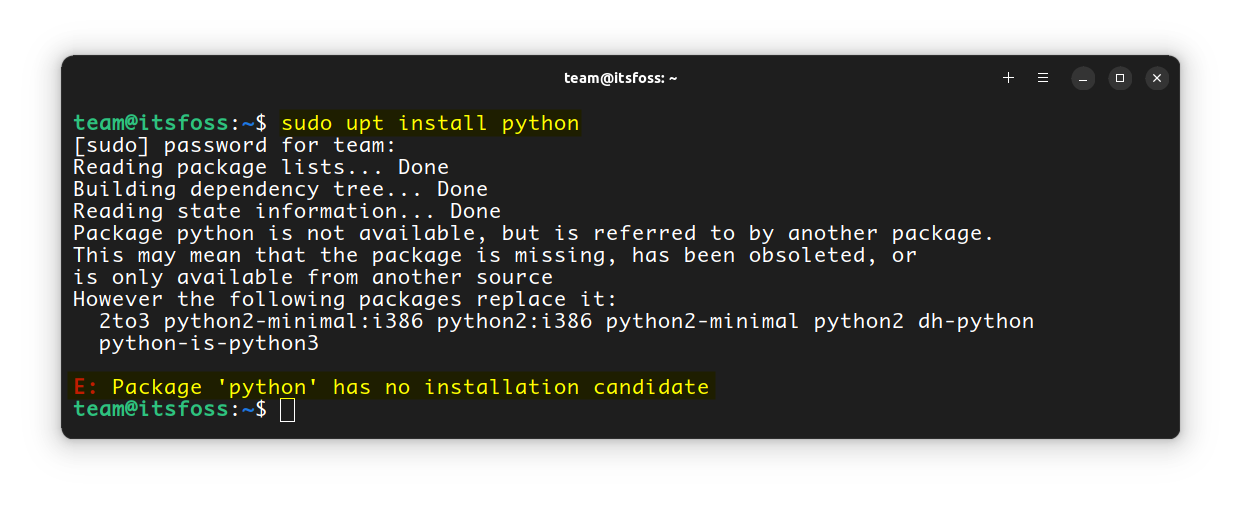
Python has no installation candidate For Ubuntu users, there is a similar tool called Nala that my interest you.
I hope you like learning about such interesting CLI tools. Stay tuned for more.